Host Specialization in Lyme Borreliosis
Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato (s.l.) is a group of 23 species of bacteria, including the etiological agents of the most frequent vector-borne disease in the Northern Hemisphere, Lyme Borreliosis (also known as Lyme Disease). They are found globally and specialized to be transmitted by >20 species of tick vectors to >200 species of different vertebrate hosts.
We conducted a literature review of >350 laboratory and field studies that identify host and vector species involved in this system. We summarized experimental methods used in the literature, rank how well each method supports a proposed association, and identified all species that have been experimentally investigated. Not only did we find that many commonly accepted associations had limited experimental support for reservoir competence, but we also found that the majority of evidence is for a select subset of host and vector species.
Check out our project publication in Ticks and Tick-borne diseases to find out more details on this complex system and learn what additional studies are needed for future efforts to predict how climate change will influence Lyme Borreliosis ecology and human health.
Find out more about Lyme Borreliosis
Test your knowledge about Lyme disease with the quiz below!
Note: ProProfs has changed their account settings and I’m aware the embedded block is not displaying properly. This will be fixed soon.
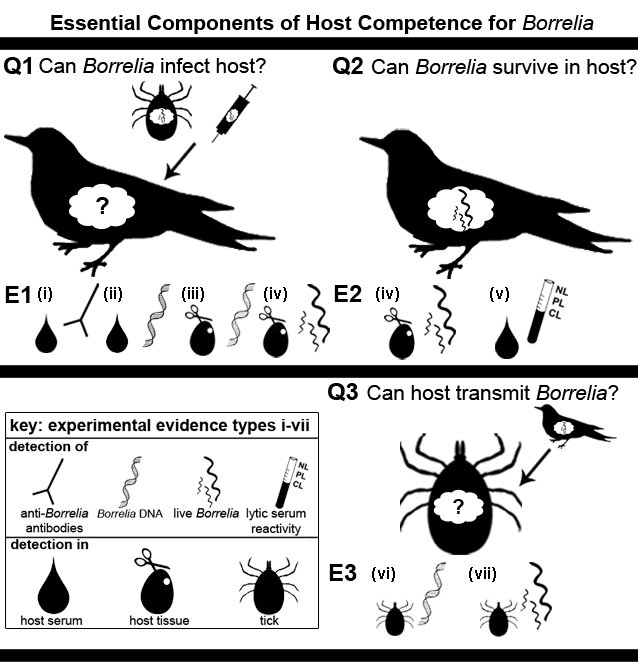
Check out this sneak preview of a figure from our recently published article that summarizes experimental evidence used to support different components of host competence for Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato
Three key components of reservoir competence for Borrelia burgodrferi sensu lato (C1-3) and the experimental evidence that is used to support them (E1-3). Three questions to determine if a potential host of Bbsl is truly reservoir competent (for all components 1-3), along with the corresponding experimental evidence that supports each question. A key to experimental evidence types (i-vii) is shown (box on left).
For a funny, easy to understand overview of the ecology behind Lyme disease in North America, check out this video by Zefrank1 that features research by many authors included in our review.
Thanks to my sister Holly Wolcott and Ile Sáenz-Soto for always being willing to give useful feedback on learning tools and visualizations as I develop them, including the Lyme Disease quiz and Reservoir Competence figures above.
Project Publication
Wolcott, Margos, Fingerle, and Becker 2021. Influence of host association on Lyme Borreliosis spirochete evolution. Ticks and Tick-borne Diseases 12(5) 101766. doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2021.101766.